PC Hardware book
Connectors used with PC Computer hardware
Connectors on the backplane of a PC Computer
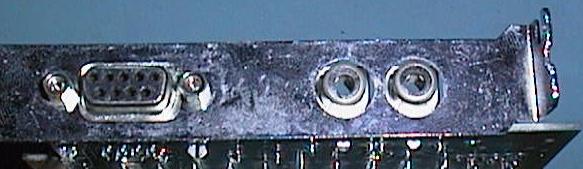
This
is the back of an old CGA video card (colour graphics adaptor)
The
left connector is a DB9S and supplies the video and sync.
signals to an RGB type monitor
The other connectors are RCA
connectors (also used on the back of audio equipment)
and these supply
composite video signals to suitable monitors

This
is the back of an old MDA video card (mono display adaptor)
The
DB25S connector on the left provides a parallel interface,
usually to a printer
The DB9S connector supplies video and
sync signals to a TTL type monitor

These
two connectors are used to provide serial interfaces
The serial
ports can use either nine pin or 25 pin DB connectors
The connector on the
left is a DB25P and the other one is a
DB9P

The
DB25S connector on the left provides a parallel port,
the
DB15S connector is the Games Port and interfaces a Joy Stick
device

The
old EGA video system also used a DB9S connector
This card also has
two RCA connectors for composite video signals
and a set of dip switches to
set up the video card
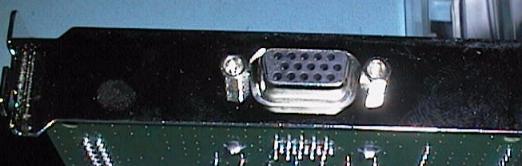
VGA
video systems use a miniature DB15S connector
This connector
is the same size as a DB9 connector but has three rows of pins

This is
the back of a network card has
A BNC coaxial connector on
the left
an RJ45 connector in the middle
and two LEDS to
show network activity on the right
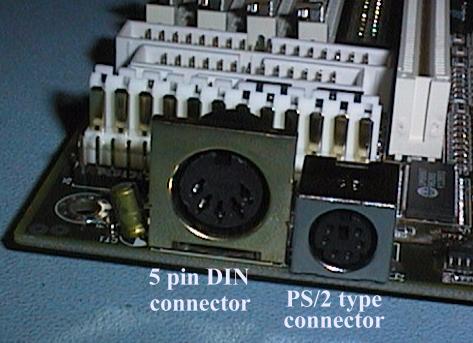
A 5 pin
DIN connector was originally used to interface the Keyboard to the computers
System Board.
This connector is also used in Audio equipment to connect Tape
Decks to Amplifiers.
More and more modern PC hardware is using a miniature
six pin DIN connector. This board has both types.
This connector is usually
called a PS/2 connector because it was first used by IBM in the PS/2 range of
computers.
Connectors inside the PC Computer
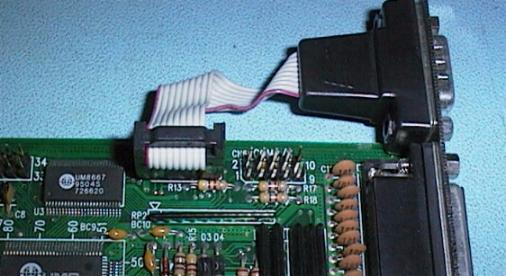
This
I/O card has two ten pin Header connectors that connect the
serial port DB connectors to the board
The board has its DB9P connector on
the backplane of the board and its DB25P on a separate backplane

The top
left 40 pin Header connector is used to connect IDE
inteface Hard Drives to this card
The right hand 34 pin
Header connector provides the Floppy Disk Drive
interface
On the lower portion of this card is an extensive
Jumper Block, used to configure the card

The 40
pin Header connector along the top of this board provides the IDE Hard Drive
interface
The 34 pin Header connector along the left hand side provides the
Floppy Drive interface
Note the two large Jumper blocks on this card

These
two connectors are used to connect to floppy disk drives
The 34 pin
Header connector on the left connects to a 3.5 inch
drive
The 34 pin Edge connector on the right
connects to a 5.25 ich drive

Power
is supplied to the System Board via this 12 pin connector

The PC
Power Supply usually has four types of connectors attached to it
The
two connectors on the left plug into the above connector on the System
Board
The disk drive connectors are the two connectors on the right
The
larger connector is used on 5 1/4 inch Floppy Disk Drives and Hard Disk
Drives
The smaller connector is used for 3 1/2 inch Floppy Disk
Drives

30
pin SIMM (single Inline Memory Modules) use this special 30 pin
socket
30 pin SIMMs provide RAM that is eight bits wide (9 bits with
parity) per module

72
pin SIMM (single Inline Memory Modules) use this larger 72 pin
socket
72 pin SIMMs provide RAM that is 32 bits wide (36 bits with
parity) per module

The
latest RAM package is the DIMM, Dual Inline Memory Module

The
DIMM package provides RAM that is 64 bits wide and uses a 168 pin edge
connector

This
image shows the ISA bus sockets (the black edge connectors)
and
The VESA local bus extension sockets (the brown sockets)
on the end of the ISA sockets

The
current local bus technology is PCI
The PCI bus uses these white
edge connectors
Note: they are not inline with the ISA slots
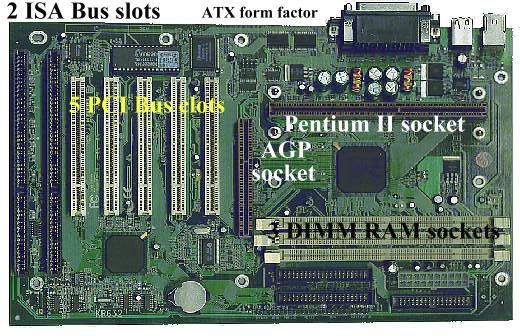
Example
of a Pentium II System Board with an AGP socket
The Advanced
Graphics Port (AGP) was introduced towards the end of 1997. This is called a
Port rather than a Bus because it is intended for a particular purpose, rather
than as a universal bus slot. AGP is based on the latest PCI specification (ver
2.1), running at 66 MHz instead of 33 MHz like all existing PCI Bus cards, and
having three extensions to the PCI specification.
The most poplar, x86 Family
XT
Computers (8086)
80286
(16 bits Data Bus)
80386
(The First 32 bits Data Bus) (Compatible with Windows`95)
80486 (High Performance)
Pentium, 5x86
and 6x86 family
Anexos
Terminology Computer Glossary
Connectors
used with PC Computer hardware
Floppy disk
drive hardware
Storage devices
The PC busses
Home

Webmaster Joel Cruz Silva e-mail: [email protected]
Tel: 53 07 835 8373
Ciudad de la Havana - Cuba





















